BIODIVERSITY-Practice Questions (3)
33. Those species whose populations have been seriously depleted and whose ultimate security is not assured are known as:
A) Threatened species
B) Endangered species
C) Vulnerable species
D) Rare species
Correct Answer: B
34.The greatest threat to global biodiversity is:
A) natural disasters such as storms.
B) pollution.
C) over exploitation of natural resources.
D) human alteration of habitats.
Correct Answer: D
35. Which of the following is threatened by illegal trade in wildlife products?
A) Nile perch
B) Elephants
C) Key deer
D) Galapagos tortoises
Correct Answer: B
36. The taxa believed likely to join the endangered category in near future is called:
A) Extinct
B) Rare
C) Vulnerable
D) Out of danger
Correct Answer: C
A) Red flowered plants
B) Red coloured fishes
C) Endangered plants and animals
D) Red eyed birds
Correct Answer: C
38. The most biodiversity rich zone in India:
A) Gangetic planes
B)Trans Himalayas
C) Western Ghats
D) Central India
Correct Answer: C
A) Core zone
B) Buffer zone
C) Manipulation zone
D) None of these
Correct Answer: B
A) 1991
B) 1995
C) 2001
D) 2007
Correct Answer: A
41. In the United States, the groups of organisms with the highest proportion of endangered or extinct species live in:
A) Grasslands
B) The deciduous forest biome
C) Freshwater habitats
D) Deserts
Correct Answer: C
42. Hotspots are regions of high:
A) Rarity
B) Endemism
C) Critically endangered population
D) Diversity
Correct Answer: B
A) Tiger
B) Musk deer
C) Elephant
D) Rhinoceros
Correct Answer: D
44. Which of the following is not done in a wild life sanctuary?
A) Fauna is conserved.
B) Flora is conserved.
C) Soil and flora is utilised.
D) Hunting is prohibited.
Correct Answer: C
45. One of the ex-situ conservation methods for endangered species is:
A) Wildlife Sanctuaries
B) Biosphere Reserves
C) Cryopreservation
D) National parks
Correct Answer: C
46. Which one of the following statement is correct for genetic diversity?
A) The total genetic information contained within all individuals of species.
B) The total phenotypic information contained within all individuals of a species.
C) The variety of life-forms on earth.
D) The variety of biotic communities in a region along with abiotic components.
Correct Answer: A
A) 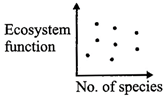
B) 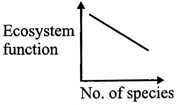
C) 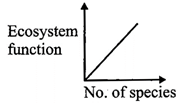
D) 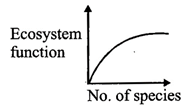
Correct Answer: D
A) Pulikat lake
B)Chilka lake
C) Sukhna lake
D) Sultanpur lake
Correct Answer: B
A) Asiatic lion
B Tiger
C) Birds
D) None of these
Correct Answer: A
A) Zoo
B) Sanctuary
C) National park
D) Biosphere reserve
Correct Answer: A
51. Which one of these is an in-situ method of conservation?
A) National park
B) Botanical garden
C) Tissue culture
D) Genetic engineering
Correct Answer: A
A) 1970
B) 1973
C) 1981
D) 1985
Correct Answer: B
A) Periyar
B) Kaziranga
C) Corbett National Park
D) Palamau
Correct Answer: C
54. Human activities such as clear-cutting and road building often create edges between areas of different habitat. Edges created by human activities:
A) are usually more abrupt than natural boundaries between habitats.
B) may have their own species not present in adjacent habitats.
C) may be dominated by relatively few species.
D) All of the above
Correct Answer: D
55. Which of the following is the main factor of desertification?
A) Tourism
B) Irrigated agriculture
C) Over-grazing
D) All of these
Correct Answer: C
Comments
Post a Comment