Changes in states of matter
What are Changes of State?
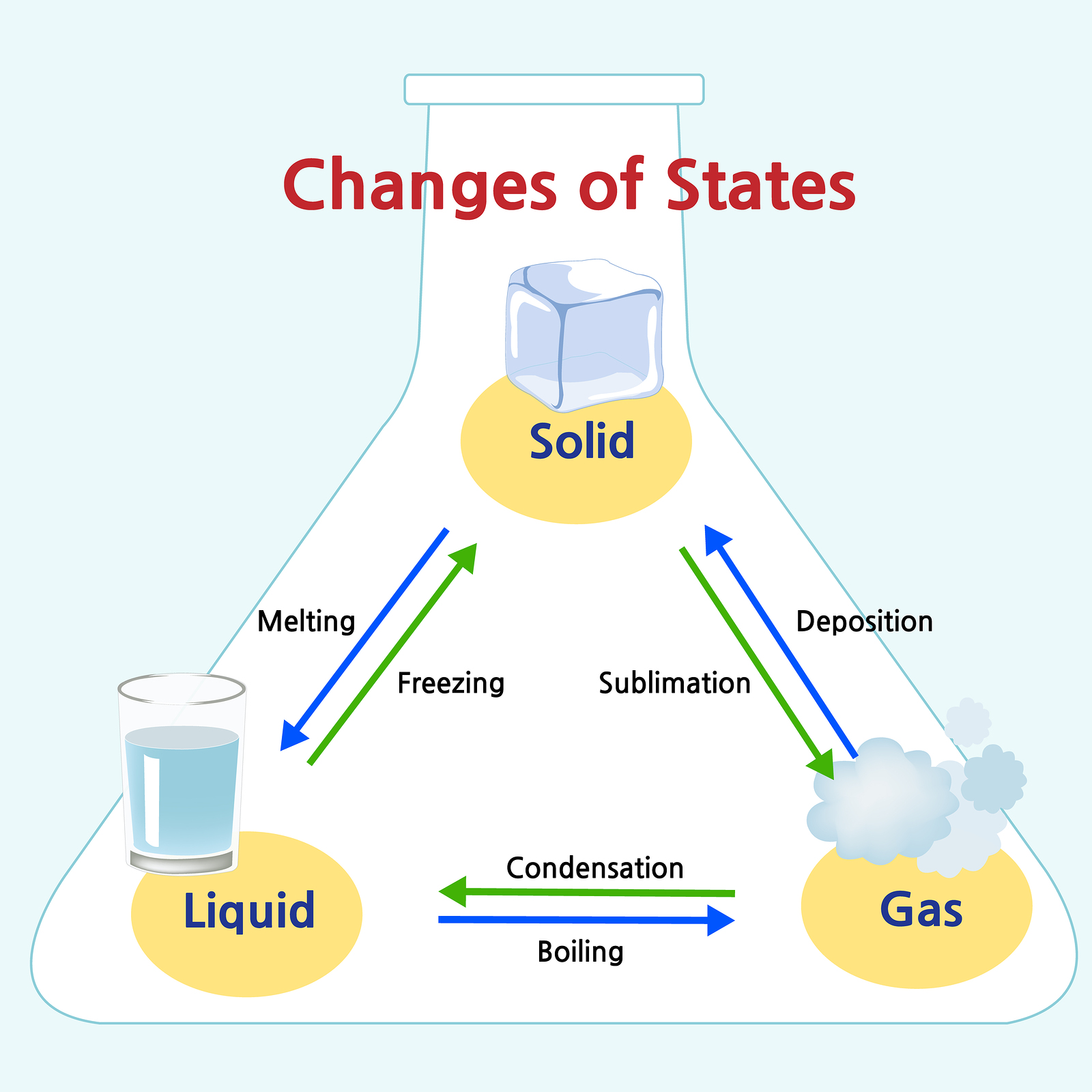
A change of state is a physical change in a matter. They are reversible changes and do not involve any changes in the chemical makeup of the matter. Common changes of the state include melting, freezing, sublimation, deposition, condensation, and vaporization.
Why do Phase Changes Occur?
When temperature or pressure change of a system occurs, phase changes occur. When the temperature or pressure increases, the interaction between the molecules increases. Similarly, when the temperature decreases, it is easier for molecules and atoms to settle into a more rigid structure.
Changes Between Liquids and Solids
How would you make ice cubes in a tray? First, you would fill the tray with water from a tap. Then you would place the tray in the freezer compartment of a refrigerator. The freezer is very cold. What happens next?
Freezing
Heat transfer occurs between the warmer tray and the colder air in the freezer. The warm water loses heat to the cold air in the freezer. This heat transfer occurs until no energy is available for the particles to slide past each other. This forces them to remain in fixed positions, locked in place by the force of attraction between them. This way liquid water is changed into solid ice. The process of liquid water changing to solid ice is termed as freezing. The temperature at which it occurs is known as freezing point.
Melting
If you took out the ice cubes from the freezer and placed them in a warm room, the ice would absorb energy from the warmer air around them. This absorbed energy would facilitate them to overcome the force of attraction holding them together, enabling them to slip out of the fixed position that they held as ice. The process in which a solids change to a liquid is called melting. The melting point is the temperature at which a solids change to a liquid.
Changes Between Liquids and Gases
If you fill a pot with cold tap water and heat it on a hot stovetop, the water heats up. Heat energy travels from the stovetop to the pot, and the water absorbs the energy from the pot. What happens to the water next?
Vaporization
If the water is hot enough, it starts to boil. Bubbles of water vapour are formed in the boiling water. This happens as particles of liquid water gain enough energy to completely overcome the force of attraction between them and change to the gaseous state. The bubbles rise through the water and escape from the pot as steam. The process in which a liquid boils and changes to a gas is called vaporization. The temperature at which a liquid boils is its boiling point.
Condensation
When you take a hot shower in a closed bathroom, the mirror is likely to fog up. You may wonder why does this happen? Some of the hot water from the shower evaporates and when it comes in contact with cooler surfaces such as the mirror, it cools and loses energy. The cooler water particles no longer have the energy to overcome the forces of attraction between them. They come together and form droplets of liquid water. This process in which a gas changes to liquid is known as condensation.
Changes Between Solids and Gases
Solids that change to gases pass through the liquid state first. However, sometimes solids change directly to gases and skip the liquid state. The reverse can also occur. Sometimes gases change directly to solids.
Sublimation
The process in which solids directly change to gases is known as sublimation. This occurs when solids absorb enough energy to completely overcome the forces of attraction between them. Dry ice is an example of solids that undergo sublimation.
Comments
Post a Comment