ANATOMY OF FLOWERING PLANTS-NEET PRACTICE QUESTIONS.
ANATOMY OF FLOWERING PLANTS
1. Which tissue is considered as most primitive both ontogenetically as well as phylogenetic ally?
A) Parenchyma
B) Collenchyma
C) Sclerenchyma
D) Aerenchyma
Correct Answer: A
2. Meristems are not found in:
A) Cycas stem
B) Pollen of Pinus
C) Fern leaf
D) Fern rhizome
Correct Answer: C
3. Healing of wound in plants takes place by activity of:
A) Intercalary meristem
B) Secondary meristem
C) Apical meristem
D) Lateral meristem
Correct Answer: B
4. The given figure shows apical meristem of root apex with few part marked as 1, 2 and 3. Identify the correct labelling of 1, 2 and 3. 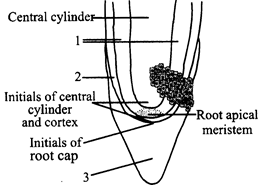
A) 1 - Vascular structure, 2 - Protoderm, 3 - Root cap
B) 1 - Cortex, 2 - Endodermis, 3 - Root cap
C) 1 - Cortex, 2 - Protoderm, 3 - Root cap
D) 1 - Tunica, 2 - Protoderm, 3 - Root cap
Correct Answer: C
5. Choose the correct option for 1 and 2.
A) 1 - Tracheid, 2 - Vessel
B) 1 - Vessel, 2 - Tracheid
C) 1 - Fibre, 2 - Tracheid
D) 1 - Fibre, 2 - Sclereid
Correct Answer: A
6.Monocot leaves grow by:
A) Apical meristem
B) Lateral meristem
C) Intercalary meristem
D) Dermatogen
Correct Answer: C
7. In the monocot root, we observe:
A) suberised exodermis, polyarch xylem, pith
B) exodermis, endarch, tetrarchclosedbundles
C) conjoint, collateral, open, polyarch vascular bundle
D) suberised exodermis, casparian strip, passage cells, cambium
Correct Answer: A
8. Match column-I with column-II and select the correct answer using the codes given below.
Column-I Column-II A. Radial vascular bundle I. Cucurbita pepo B. Collateral vascular bundle II. Dracaena C. Bicollateral vascular bundle III. Roots of angiosperms D. Amphicribral vascular bundle IV. Sunflower stem E. Amphivasal vascular bundle V. fern
| Column-I | Column-II | ||
| A. | Radial vascular bundle | I. | Cucurbita pepo |
| B. | Collateral vascular bundle | II. | Dracaena |
| C. | Bicollateral vascular bundle | III. | Roots of angiosperms |
| D. | Amphicribral vascular bundle | IV. | Sunflower stem |
| E. | Amphivasal vascular bundle | V. | fern |
A) A-III; B-IV; C-I; D-V; E-II
B) A-II; B-III; C-I; D-V; E-IV
C) A-III; B-IV; C-V; D-I; E-II
D) A-III; B-I; C-II; D-IV; E-V
Correct Answer: A
9. In the given columns, column-I contain structures of plant and column-II contain its feature. Select the correct match.
Column-I Column-II A. Lateral I. Fascicular vascular meristem cambium, inter fascicular cambium and cork cambium. B. Apical meristem II. Produces dermal tissue, ground tissues and vascular tissue. C. Bast fibres III. Generally absent in primary phloem but found in secondary phloem. D. Sap wood IV. Involved in the conduction of water and minerals from the root to leaf.
| Column-I | Column-II | ||
| A. | Lateral | I. | Fascicular vascular meristem cambium, inter fascicular cambium and cork cambium. |
| B. | Apical meristem | II. | Produces dermal tissue, ground tissues and vascular tissue. |
| C. | Bast fibres | III. | Generally absent in primary phloem but found in secondary phloem. |
| D. | Sap wood | IV. | Involved in the conduction of water and minerals from the root to leaf. |
A) A-I; B-II; C-III; D-IV
B) A-III; B-I; C-II; D-IV
C) A-I; B-IV; C-III; D-II
D) A-II; B-IV; C-III; D-I
Correct Answer: A
10. Which one of the following statement is correct about bull form/motor cell?
A) It is seen in grasses.
B) It is large-sized, thin-walled colourless, vacuolated cells on the ad axial surface.
C) It helps in rolling of leaf to minimise water loss when it is flaccid.
D) All of the above
Correct Answer: D
11. A scion is grafted to a stock. The quality of fruits produced will be determined by the genotype of:
A) Stock
B) Scion
C) Both stock and scion
D) Neither stock nor scion
Correct Answer: B
A) inter fascicular position
B) multicellular nature
C) gravitational force
D) difference in supply of hormones on two sides
Correct Answer: A
13. Which of the following plant shows multi epidermis?
A) Croton
B) Allium
C) Nerium
D) Cucurbita
Correct Answer: C
14. Identify types of vascular bundles in given figures 1, 2 and 3. 
A) 1- Radial 2- Conjoint closed 3- Conjoint open
B) 1- Conjoint closed 2- Conjoint open 3- Radial
C) 1- Conjoint open 2- Conjoint 3- Radial
D) 1- Bicol lateral 2- Concentric 3- Radial
Correct Answer: A
15. Red brasilin comes from which part of Caesalpinia sappan?
A) Bark only
B) Heart wood only
C) Sap wood and bark
D) Heart wood and bark
Correct Answer: B
A) Gums
B) Resins
C) Tannins
D) Mucilages
Correct Answer: C
17. A boy standing behind the tree carved his name on the tree, after twenty years:
A) height of the carved name increased.
B) the name was not there as it gets abolished due to secondary growth.
C) the height of carved name remain the same.
D) the height of the carved name decreased.
Correct Answer: C
18. A dendrochronologist observed total 22 ring of spring wood and autumn wood in a dicot stem in 1998. How many annual rings will be observed by him in 2007?
A) 21
B) 25
C) 20
D) 30
Correct Answer: C
19. Bamboo and grasses elongate by the activity of:
A) Apical meristem
B) Lateral meristem
C) Secondary meristem
D) Intercalary meristem
Correct Answer: D
20. Meristematic tissues are composed of :
A) mature cell
B) fully differentiated cell
C) cells that cannot divide
D) immature cells with power to divide
Correct Answer: D21. Which one of the following option shows the correct labelling of the parts marked as 1, 2, 3 and 4 in the given figure of a typical dicot root? 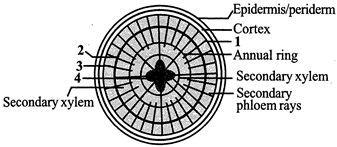

AA ) 1 - Primary phloem, 2 - Vascular cambium, 3 - Secondary phloem, 4 - Primary xylem
B) 1 - Secondary phloem, 2 - Vascular cambium, 3 - Primary phloem, 4 - Primary xylem
C) 1 - Primary phloem, 2 - Primary xylem, 3 - Secondary phloem, 4- Vascular cambium
D) 1 - Secondary phloem, 2 - Primary xylem, 3 - Primary phloem, 4 - Vascular cambium
Correct Answer: A
22. Largest number of chloroplast is found in:
A) Palisade tissue
B) Spongy tissue
C) Transfusion tissue
D) Bundle sheath cells
Correct Answer: A
23.If a stem is girdled:
A) root dies first
B) shoot dies first
C) Both die together
D) Neither root nor shoot would die
Correct Answer: A
24. In dicotyledonous stem, fascicular cambium is a meristematic tissue. It is an example of which of the following meristem?
A) Lateral
B) Secondary
C) Apical
D) Intercalary
Correct Answer: A
25. Which of the following statement(s) is/are incorrect?
(i) Cork cambium is also called phellogen. (ii) Cork is also called phellem. (iii) Secondary cortex is also called periderm. (iv) Cork cambium, cork and secondary cortex are collectively called phelloderm.
| (i) Cork cambium is also called phellogen. |
| (ii) Cork is also called phellem. |
| (iii) Secondary cortex is also called periderm. |
| (iv) Cork cambium, cork and secondary cortex are collectively called phelloderm. |
A) (iii) and (iv)
B) (i) and (ii)
C) (ii) and (iii)
D) (ii) and (iv)
Correct Answer: A
26. Which of the following statement is correct about heart wood/duramen?
(i) It does not help in water and mineral conduction. (ii) It is dark coloured but soft. (iii) It has treachery elements filled with tannins, resins, gums, oil, etc. (iv) It is a peripheral part. (v) They are sensitive to microbes and insects, hence least durable.
| (i) It does not help in water and mineral conduction. |
| (ii) It is dark coloured but soft. |
| (iii) It has treachery elements filled with tannins, resins, gums, oil, etc. |
| (iv) It is a peripheral part. |
| (v) They are sensitive to microbes and insects, hence least durable. |
A) (i) and (iii)
B) (ii) and (iii)
C) (iv) and (v)
D) (iii) and (iv)
Correct Answer: A
27. T.S. of dicot stem is given below, certain parts have been indicated by alphabets. Choose the correct option. 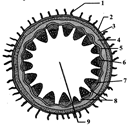
A) 1 - Epidermis, 2 - Epidermal hairs, 3 - Parenchyma, 4 - Starch Sheath, 5 - Hypodermis (collenchyma), 6 - Vascular bundle, 7 - Bundle cap, 8 - Medulla or pith, 9 - Medullary rays
B) 1 - Epidermal hairs, 2 - Epidermis, 3 - Hypodermis (collenchyma), 4 - Parenchyma, 5 - Starch sheath, 6 - Bundle cap, 7 - Vascular bundle, 8 - Medullary rays, 9 - Medulla or pith
C) 1 - Epidermal hairs, 2 - Epidermis, 3 - Hypodermis (collenchyma), 4 - Starch sheath, 5 - Parenchyma, 6 - Vascular bundle, 7 - Bundle cap, 8 - Medulla or pith, 9 - Medullary rays
D) 1 - Epidermal hairs, 2 - Epidermis, 3 - Parenchyma, 4 - Hypodermis (collenchyma), 5 - Starch sheath, 6 - Vascular bundle, 7 - Bundle cap, 8 - Medulla or pith, 9 - Medullary rays
Correct Answer: B
28.
Match the terms given in column-I with their features given in column-II and choose the correct option.Column-I (Terms) Column-II (Features) A. Fibres I. Cells are living and thin walled with cellulosic cell wall, store food materials in the form of starch or fat. B. Sclereids II. Main water conductive cells of the pteridophytes and the gymnosperms. C. Tracheids III. Thick walled, elongated and pointed cells, generally occurring in groups. D. Vessels IV. Long cylindrical tube like structure and cells are devoid of protoplasm. Characteristic feature of angiosperms. E. Xylem V. Reduced form of parenchyma sclerenchyma cells with highly thickened lignified cellular walls that form small bundles of durable layers of tissue in most plants.
| Column-I (Terms) | Column-II (Features) | ||
| A. | Fibres | I. | Cells are living and thin walled with cellulosic cell wall, store food materials in the form of starch or fat. |
| B. | Sclereids | II. | Main water conductive cells of the pteridophytes and the gymnosperms. |
| C. | Tracheids | III. | Thick walled, elongated and pointed cells, generally occurring in groups. |
| D. | Vessels | IV. | Long cylindrical tube like structure and cells are devoid of protoplasm. Characteristic feature of angiosperms. |
| E. | Xylem | V. | Reduced form of parenchyma sclerenchyma cells with highly thickened lignified cellular walls that form small bundles of durable layers of tissue in most plants. |
A) A - I; B - II; C - III; D - IV; E - V
B) A - III; B -V; C - II; D - IV; E - I
C) A - III; B - I; C - V; D - II; E - IV
D) A - V; B - IV; C - III; D - I; E - II
Correct Answer: B
29. Read the following statements and select the correct one(s) from the options.
(i) In flowering plants, tracheid and vessels are the main water transporting elements. (ii) The presence of vessels is a characteristic feature of angiosperms. (iii) Xylem fibres have highly thinned walls and their cell walls are made up of cellulose. (iv) Xylem parenchyma store food materials in the form of starch or fat and other substances like tannins.
| (i) In flowering plants, tracheid and vessels are the main water transporting elements. |
| (ii) The presence of vessels is a characteristic feature of angiosperms. |
| (iii) Xylem fibres have highly thinned walls and their cell walls are made up of cellulose. |
| (iv) Xylem parenchyma store food materials in the form of starch or fat and other substances like tannins. |
A) Only (i)
B) Both (ii) and (iii)
C) Both (iii) and (iv)
D) (i), (ii) and (iv)
Correct Answer: D
30. All the following statements regarding sieve tube elements are correct except that:
A) their end walls have perforated sieve plates which become impregnated with lignin at maturity.
B) they possess peripheral cytoplasm as well as a large vacuole.
C) distinct proteinaceous inclusions, the P-proteins are seen evenly distributed throughout the lumen.
D) long, slender, tube-like structures arranged in longitudinal series.
Correct Answer: A
31. The lacunae in vascular bundles of monocot stems are:
A) Metaxylem
B) Mucilagenous canal
C) Lysigenous water cavity
D) Large-sized vessel
Correct Answer: C
32.From where the commercial jute fibres are obtained?
A) Interxylary fibres
B) Xylem fibres
C) Phloem fibres
D) None of these
Correct Answer: C
33. Abnormal secondary growth is observed in:
A) Dracaena
B) Wheat
C) Ginger
D) Rice
Correct Answer: A
34. The trees growing in deserts will:
A) show alternate rings of xylem and sclerenchyma.
B) show distinct annual rings.
C) not show distinct annual rings.
D) have only conjunctive tissue and phloem formed by the activity of cambium.
Correct Answer: C
35. Choose the correct option for T.S. of monocot root. 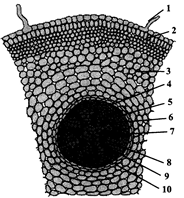
A) 1 - Root hair, 2 - Epiblema, 3 - Cortex, 4 - Endodermis, 5 - Passage cell, 6 - Pericycle, 7 - Pith, 8 - Phloem, 9 - Metaxylem, 10 - Protoxylem
B) 1 - Root hair, 2 - Epiblema, 3 - Cortex, 4 - Endodermis, 5 - Passage cell, 6 - Pith, 7 - Pericycle, 8 - Metaxylem, 9 - Phloem, 10 - Protoxylem
C) 1 - Root hair, 2 - Epiblema, 3 - Cortex, 4 - Endodermis, 5 - Pericycle, 6 - Passage cell, 7 - Phloem, 8 - Pith, 9 - Protoxylem, 10 - Metaxylem
D) 1 - Root hair, 2 - Cortex, 3 - Epiblema, 4 - Pericycle, 5 - Endodermis, 6 - Pith, 7- Passage cell, 8 - Phloem, 9 - Protoxylem, 10 - Metaxylem
Correct Answer: A
36. Gaseous exchange between air and internal tissues of old corky stem takes place through:
A) Pits
B) Stomata
C) Lenticels
D) Sieve plates
Correct Answer: C
37. In roots of monocotyledon, the histogen present at the apex of the root tip is:
A) Dermatogen
B) Procambium
C) Calyptrogen
D) Plerome
Correct Answer: C
38. Active divisions occur in the cells of:
A) Xylem
B) Phloem
C) Cambium
D) Collenchyma
Correct Answer: C
39. What happens in plants during vascularisation?
A) Differentiation of procambium, formation of primary phloem followed by formation of primary xylem.
B) Differentiation of procambium followed by the formation of primary phloem and xylem simultaneously.
C) Formation of procambium, primary phloem and xylem simultaneously.
D) Differentiation of procambium followed by the formation of secondary xylem.
Correct Answer: B
40. In Cucurbita, stem vascular bundles are:
A) Radial
B) Collateral
C) Concentric
D) Bicollateral
Correct Answer: D
41. In Bougainvillea, the primary vascular bundles lie scattered. A cambium ring is formed:
A) from the pericycle
B) from intra fascicular cambium
C) just outside the primary bundles
D) by inter and intra fascicular cambia
Correct Answer: C
42. When phloem and cambium are present on both sides of xylem, the vascular bundle is called:
A) Bicollateral
B) Radial
C) Concentric
D) Collateral
Correct Answer: A
43. Which of the following figure is a type of permanent tissue having many different types of cell?
A) 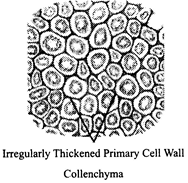
B) 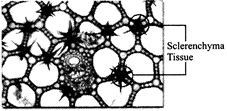
C) 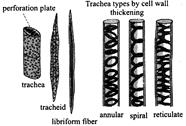
D) 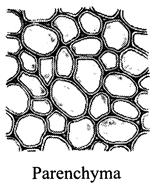
Correct Answer: C
44. Match column-I with column-II and select the correct answer using the options given below.
Column-I Column-II A. Xylem vessels I. Store food materials B. Xylem tracheids II. Obliterated lumen C. Xylem fibre III. Perforated plates D. Xylem parenchyma IV. Chisel-like ends
| Column-I | Column-II | ||
| A. | Xylem vessels | I. | Store food materials |
| B. | Xylem tracheids | II. | Obliterated lumen |
| C. | Xylem fibre | III. | Perforated plates |
| D. | Xylem parenchyma | IV. | Chisel-like ends |
A) A-IV; B-III; C-II; D-I
B) A-III; B-II; C-I; D-IV
C) A-II; B-I; C-IV; D-III
D) A-III; B-IV; C-II; D-I
Correct Answer: D
45. Which of the following statement(s) is/are correct?
(i) Uneven thickening of cell wall is characteristic of sclerenchyma. (ii) Periblem forms cortex of the stem and the root. (iii) Tracheids are the chief water transporting elements in gymnosperms. (iv) Companion cell is devoid of nucleus at maturity. (v) The commercial cork is obtained from Quercus suber.
| (i) Uneven thickening of cell wall is characteristic of sclerenchyma. |
| (ii) Periblem forms cortex of the stem and the root. |
| (iii) Tracheids are the chief water transporting elements in gymnosperms. |
| (iv) Companion cell is devoid of nucleus at maturity. |
| (v) The commercial cork is obtained from Quercus suber. |
A) (i) and (iv) only
B) (ii) and (v) only
C) (iii) and (iv) only
D) (ii), (iii) and (v) only
Correct Answer: D
46. How many growth rings should be develop per year in a plant grown in Rajasthan with four distinct seasons (viz, summer, rain, winter and spring)?
A) Four
B) Two
C) One
D) None of these
Correct Answer: B
47. Extrastelar secondary growth takes place by:
A) Vascular cambium
B) Phellogen
C) Phellem
D) Phelloderm
Correct Answer: B
48. The cork of commerce comes from:
A) Quercus suber
B) Quercus incana
C) Quercus ithaburensis
D) All of the above
Correct Answer: A
49. The pneumatophores have openings called:
A) Stomata
B) Lenticels
C) Hydathodes
D) All of these
Correct Answer: B
50.Phloem parenchyma are absent in:
A) Dicots
B) Monocots
C) Gymnosperms
D) All of these
Correct Answer: B
51. Match column-I with column-II and choose the correct option.
Column-I Column-II A. Spring wood or wood I. Lighter in colour early B. Autumn wood or late wood II. High density III. Low density IV. Darker in colour V. Larger number of xylem elements VI. Vessels with wider cavity VII. Lesser number of xylem elements VIII. Vessels with small cavity
Which of the following combination is correct?
| Column-I | Column-II | ||
| A. | Spring wood or wood | I. | Lighter in colour early |
| B. | Autumn wood or late wood | II. | High density |
| III. | Low density | ||
| IV. | Darker in colour | ||
| V. | Larger number of xylem elements | ||
| VI. | Vessels with wider cavity | ||
| VII. | Lesser number of xylem elements | ||
| VIII. | Vessels with small cavity |
A) A - II; IV; VII; VIII; B - I; III; V; VI
B) A - I; II; VII; VIII; B - III; IV; V; VI
C) A - I; III; V; VI; B - II; IV; VII; VIII
D) A - I; III; VII; VIII; B - II; IV; V; VI
Correct Answer: C
52. In monocots, root cap is formed by:
A) Dermatogen
B) Calyptrogen
C) Wound cambium
D) Vascular cambium
Correct Answer: B
53. In woody dicotyledons, the arrangement of vessels is either diffuse porous or ring porous. Based on the these data, which one of the following statements is correct?
A) Ring porous vessels are specialised and are used for conducting more water for a shorter period only, when trioses occur early in the vessels.
B) Although diffuse porous vessels are not so specialised as ring porous vessels, they conduct more water at all periods and through new xylem vessels added gradually during development.
C) Diffuse porous vessels carry more water and also faster because of a greater number of small vessels having greater capillary force.
D) Ring porous vessels conduct more water as they are formed early during development, when the need for water is great.
Correct Answer: D
54. Periderm is formed from:
A) Vascular cambium
B) Phellogen
C) Fascicular cambium
D) Interfascicular cambium
Correct Answer: B
55. Annual rings are the bands of:
A) secondary cortex and cork
B) all secondary vascular tissues
C) secondary xylem and xylem rays
D) secondary phloem and medullary rays
Correct Answer: C
56. Secondary growth in the dicot stems is possible because of the presence of:
A) Xylem
B) Phloem
C) Cambium
D) Medullary rays
Correct Answer: C
57. Which of the following meristem is responsible for extrastelar secondary growth in dicotyledonous stem?
A) Phellogen
B) Intra fascicular cambium
C) Inter fascicular cambium
D) Intercalary meristem
Correct Answer: A
58. Periblem form:
A) Endodermis
B) Cortex
C) Both (a) and (b)
D) Epidermis
Correct Answer: C
59. Identify 1, 2 and 3 in the given figure of shoot apical meristem 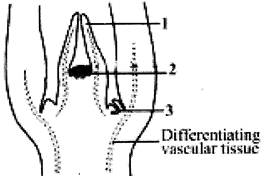
A) 1 - Leaf primordium, 2 - Shoot apical meristem, 3 - Axillary bud
B) 1 - Leaf primordium, 2 - Shoot apical meristem, 3 - Apical bud
C) 1 - Root hair primordium, 2 - Root apical meristem, 3 - Axillary bud
D) 1 - Root hair primordium, 2 - Root apical meristem, 3 - Terminal bud
Correct Answer: A
60. Select the combination of correct statements from the options given below.
(i) Annual rings are formed as a result of seasonal environmental conditions. (ii) Tracheid's/vessels elements are larger during periods when water is abundant. (iii) Tracheid's/vessels elements have thicker wall during periods of water deprivation. (iv) Wood formed in the previous years is darker than newer wood.
| (i) Annual rings are formed as a result of seasonal environmental conditions. |
| (ii) Tracheid's/vessels elements are larger during periods when water is abundant. |
| (iii) Tracheid's/vessels elements have thicker wall during periods of water deprivation. |
| (iv) Wood formed in the previous years is darker than newer wood. |
A) (i) and (ii)
B) (ii) and (iv)
C) (i), (ii) and (iii)
D) (ii), (iii) and (iv)
Correct Answer: C
Comments
Post a Comment